The Administration and Development Branch provides various management and support services to the Department. These include staff management and development, financial management, information technology, planning and implementation of capital works projects, outsourcing of services, complaints management, public education and publicity on environmental hygiene and food safety.
Grade Management
There are three major grades covering Health Inspectors, Hawker Control Officers and Foremen. There are two grade managers, one for Health Inspector grade and another for Hawker Control Officer and Foreman grades. The grade managers are responsible for staff matters involving manpower planning, career development, postings, promotion and training.
The Health Inspector grade comprises six non-directorate ranks - Senior Superintendent, Superintendent, Chief Health Inspector, Senior Health Inspector, Health Inspector I/II, and Student Health Inspector. They are responsible for various environmental hygiene and food safety functions, such as handling of environmental nuisance cases, licensing, prosecution, meat inspection, cleansing services, outsourcing, pest control, hawker control, management of markets, cemeteries and crematoria, food control and health education.
The Hawker Control Officer grade comprises five ranks - Principal Hawker Control Officer, Chief Hawker Control Officer, Senior Hawker Control Officer, Hawker Control Officer and Assistant Hawker Control Officer. They are responsible for controlling on-street hawking activities, managing hawker permitted places and taking law enforcement action against illegal hawking activities. They are also empowered to take legal action against people committing cleanliness offences, such as littering and spitting.
The Foreman grade comprises four ranks - Senior Overseer, Overseer, Senior Foreman and Foreman. They are mainly responsible for supervising the work of minor staff in market management, street cleansing, waste collection, pest control and monitoring the performance of the Department's service contractors. Members of the grade can also take legal action against cleanliness offenders.
Training
Vocational and general training is provided to staff to equip them with the necessary knowledge and skills to carry out their duties, to enhance professionalism and help them gain the pre-requisite qualifications for career advancement. Staff are provided with in-house programmes and those organised by local and overseas institutes.
In-house programmes are mainly designed, administered and conducted by the Department's Training Section. In 2006, 435 in-house classes were organised for 10,470 trainees, involving a total of 14,612 trainee-days.
Local academic institutes are appointed to administer and conduct commissioned programmes. Some of these lead to the award of qualifications that are pre-requisites for career advancement. Staff members are also sponsored to attend local open programmes that are highly relevant to the Department's work. Altogether, 231 classes were organised for 4,549 trainees, making a total of 6,740 trainee-days.
In addition, officers are sponsored to attend local or international management development programmes. In 2006, a total of 42 trainees were placed on 27 training programmes outside Hong Kong, involving 423 trainee-days.
Management Services
Management consultancy and statistical services essentially make up the work of Management Services. The services help management improve the delivery of public services, monitor the standard of performance, and formulate policy in the provision of services and staffing.
Six major management studies were completed during the year - "Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) Study for Central Uniform Store", "Review of Street Washing Services (2005)", "BPR Study on Computerisation of Food Sampling", "BPR Study on Computerisation of Agricultural Chemicals and Veterinary Drugs Unit", "Implementation of the Review of Manual Gully Cleansing Service" and "BPR Study on Contractors' Workers Record System". In addition, a number of statistical surveys were conducted on issues such as the effectiveness of printed health education publicity material, the food purchasing habits of households, the evaluation of food hygiene campaign seminars, genetically modified food workshops and consumers' perception on food risk.
Ongoing consultancy services are provided to assist the implementation of recommendations of various studies, support the development and operation of a bar-coding file management system, and improve the design of departmental forms. Technical advice is offered to help client sections to undertake statistical surveys and analyse the data collected.
Financial Management
Breakdown of Expenditure by Expenditure Group (Chart)
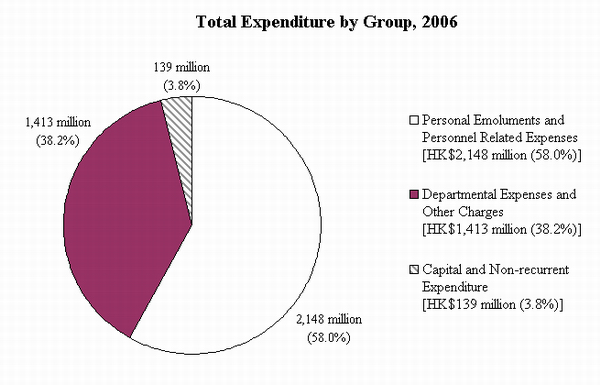
| $M | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Emoluments and Personnel Related Expenses |
2,148
|
58.0%
|
| Departmental Expenses and Other Charges |
1,413
|
38.2%
|
| Capital and Non-recurrent Expenditure |
139
|
3.8%
|
Breakdown of Expenditure by Activities (Chart)
Note: Figure may not add up to total due to rounding.
| $M | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
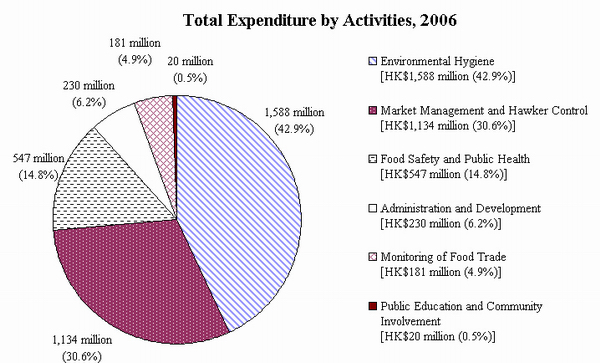
| Environmental Hygiene |
1,588
|
42.9%
|
| Market Management and Hawker Control |
1,134
|
30.6%
|
| Food Safety and Public Health |
547
|
14.8%
|
| Administration and Development |
230
|
6.2%
|
| Monitoring of Food Trade |
181
|
4.9%
|
| Public Education and Community Involvement |
20
|
0.5%
|
Breakdown of Revenue (Chart)

|
$M
|
Percentage
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Market Stall Rental |
333
|
46.8%
|
| Licences and Permit Fees |
239
|
33.6%
|
| Other Revenue |
140
|
19.6%
|
All matters relating to expenditure and procurement, including payment processing, financial advice and monitoring, are handled by the Finance and Supplies Division.
In 2006, the Department spent $3,700 million, including $2,148 million on salaries and allowances and personnel related expenses, $1,413 million on departmental expenses and other charges, and
$139 million on capital and non-recurrent expenditure.
By activities, the majority of the expenditure ($1,588 million) was on environmental hygiene. This was followed by $1,134 million for market management and hawker control, $547 million for food safety and public health, $230 million for administration and development, $181 million for monitoring the food trade, and $20 million for public education and community involvement.
In 2006, the Department received revenue of $712 million. Most of the revenue came from the rental of stalls in public markets managed by the Department ($333 million) and from licence and permit fees ($239 million). Other sources included fees for cemeteries and crematoria services ($67 million), fees for meat examination ($27 million) and other miscellaneous services ($46 million).
Information Technology
The Department uses information technology extensively to provide high quality services to the public. During 2006:
- The government-wide Accessibility Programme has been completed. Staff who previously did not have access to networked office automation personal computers are now provided with shared network personal computers installed with office automation software, Government-to-Employee (G2E) and Government-to-Government (G2G) computer applications and Internet access capability.
- The licence and permit system was upgraded to provide more functions in processing applications for various restaurant licences, places of public entertainment licences, liquor licences, food permits and karaoke establishment permits and to automate more existing manual procedures to improve the efficiency of office operations.
Capital Works
In the Government's 2006 Capital Works Resource Allocation Exercise, the five-year allocation on food and environmental hygiene services capital projects is estimated at $1,910 million. Of the total allocation, about $650 million is to meet expenditure on projects under construction or completed with outstanding accounts, while $1,260 million has been earmarked for new projects.
Markets
Construction of the new shopping kiosks to replace the Stanley Temporary Market was completed in 2006 and the new kiosks will be opened in January 2007. In 2006, two new markets were under construction.
During the year, improvement works to the following markets and Cooked Food Centres (CFCs) were completed-
- retrofitting of air-conditioning in the San Hui Market in addition to general improvements, with support of 85% of the tenants or more; and
- essential improvements to tie in with the latest building and fire safety requirements and other general works in the Aberdeen Market and CFC, Ngau Chi Wan Market and CFC, and Ngau Tau Kok Market and CFC.
Works for the retrofitting of air-conditioning in addition to general improvements for the Fa Yuen Street Market and CFC projects are in the planning stage.
Refuse Collection Points
As part of the continuing efforts to improve Hong Kong's living environment, the Department is replacing temporary roadside Refuse Collection Points (RCPs) with off-street facilities in enclosed buildings equipped with modern de-odorising installations. The enlargement of RCP at Shung Yan Street in Kwun Tong and the construction of RCP at Yee Kuk Street in Sham Shui Po were completed during the year. Construction work for the RCP at Tat Yan Square in Tuen Mun commenced at end of 2006.
Public Toilets
New public toilets were completed at Kowloon Tong Public Transport Interchange in Kowloon Tong, Tsam Chuk Wan at Sai Kung, Stanley Municipal Services Building and Stanley Waterfront in Southern District as well as Yee Kuk Street in Sham Shui Po.
Construction of new public toilets is in progress for the new Tsim Sha Tsui East Public Transport Interchange in Yau Tsim District, the new Ma On Shan Rail Tai Wai Station Public Transport Interchange, Ma Liu Shui Waterfront and Science Park Road in Sha Tin, Fo Yin Road and Chong San Road in Tai Po, the new Lok Ma Chau Spur Line Public Transport Interchange and the new Shenzhen Western Corridor in Yuen Long, the New Wan Chai Market in Wan Chai and Sheung On Street in Chai Wan.
Under the Public Toilet Improvement Programme, 10 public toilet/aqua privy improvement projects were completed in 2006 and improvements to around 30 are in progress or being planned.
Under the capital works project for conversion of 100 aqua privies into flushing toilets initiated by the former Team Clean, 30 aqua privies were converted into flushing toilets in 2006, on top of the 8 aqua privies completed in 2005. Conversion of the remaining 62 aqua privies is in progress or being planned.
Cemeteries and Crematoria
The replacement of the six cremators at the Diamond Hill Crematorium is in progress, with work on Phases I and II scheduled for completion by early 2007 and late 2008 respectively. Planning is under way for the reprovisioning of the Wo Hop Shek and Cape Collinson Crematoria. The construction
of 7,000 niches at Kwai Chung, Cape Collinson and Wo Hop Shek Columbaria was completed in 2006.
Outsourcing of Services
Contracts (Chart)
| Services Contracted Out | No. | $M |
|---|---|---|
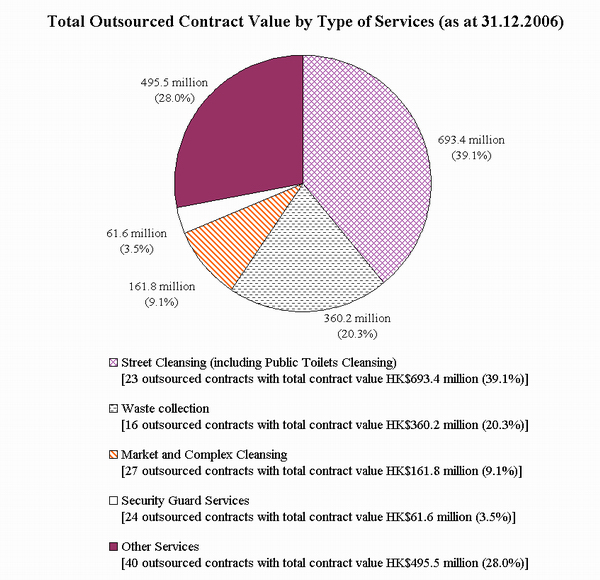
| Street Cleansing (including Public Toilets Cleansing) | 23 | 693.4 |
| Waste Collection | 16 | 360.2 |
| Market and Complex Cleansing | 27 | 161.8 |
| Security Guard Services | 24 | 61.6 |
| Other Services | 40 | 495.5 |
By the end of 2006, 130 contracts valued at $1,772.5 million were in force for the provision of services by private contractors. The outsourcing policy is aimed at greater cost-effectiveness and efficiency in the delivery of services.
Examples of outsourcing services include public market cleansing, street cleansing, waste collection, mechanical street sweeping, mechanical gully cleansing, building cleansing, security guard services, pest control services, animal carcass collection, cleansing and undergrowth cutting services for cemeteries and columbaria, and the collection of recyclables.
Measurable performance standards are written into the contracts to ensure the quality of services provided. Protective clauses have also been included in tenders to safeguard the rights and benefits of non-skilled workers. Supervisory checks are conducted to ensure compliance by contractors.
Complaints Management
The Complaints Management Section is responsible for formulating and reviewing policies on, and procedures for, handling all types of complaints. During the year, 153,000 complaints were received by the Department, including 151,699 relating to the services it provides.
The section conducts independent investigations into staff-related complaints. In addition to taking immediate follow-up action on the complaints and replying to complainants, the section analyses the complaints according to their type, nature and causes to enable remedial action or improvements to be taken.
Quality Assurance
Continuous improvement is one of the priority tasks of the Department to ensure provision of quality services to the public.
The Quality Assurance Section is mainly responsible for conducting day-to-day regulatory inspections on services provided by the Department and service contractors. Recommendations are made for improvements to services where inadequacies in existing operational systems, procedures and guidelines are identified. The section also recommends good performers for Quality Assurance Awards to motivate meritorious and hardworking front-line staff. In addition, the section investigates staff-related cases of dereliction of duty and employment-related complaints of service contractors in an independent, objective and fair manner.
Public Education and Publicity
Public education plays an important role in almost all the Department's activities and initiatives, forming part of an integrated approach to ensuring food safety and improving environmental hygiene. To achieve this, the Department organises publicity and educational programmes, and arranges exhibitions, outreaching programmes and seminars for the general public to enhance their awareness of these issues.
The Department operates the Communication Resource Unit at the Fa Yuen Street Municipal Services Building in Mong Kok and the Health Education Exhibition and Resource Centre inside Kowloon Park in Tsim Sha Tsui.
The Health Education Exhibition and Resource Centre provides group visits and guided tours to schools, voluntary agencies and the public. Seminars and activities are also conducted regularly. During the year, the Centre attracted 149,993 visitors, and organised 1,116 talks, exhibitions and activities for kindergartens, primary schools and secondary schools; 920 talks for elderly centres; and 373 talks for members of the general public. Audio-visual aids, question-and-answer sessions, demonstrations and games were used to enrich and enliven the learning process. The Centre also launched the Mobile Education Centre (a publicity vehicle) in the last quarter of 2006 to enhance its outreaching efforts in promoting food safety and environmental hygiene to the public. For the Communication Resource Unit, school talks and talks for the general public were organised in 2006.
On food safety, various publicity and educational programmes were organised on nutrition labelling, genetically modified (GM) food, the HACCP system (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point), "poon choi" and "catering services for the elderly homes". Train-the-trainer workshops on nutrition labelling and GM food were organised for members of youth centres, women's associations and parent-teacher associations.
To cater for the specific needs of the food trade, seminars on restaurant licensing were arranged on a bi-monthly basis for those who had applied for licences for food premises or who considered starting a food business.
On environmental hygiene, the Department continued its publicity efforts in 2006, which included special radio and television messages, banners, posters and pamphlets. Anti-rodent and anti-mosquito campaigns were organised to solicit public support and participation in controlling pests.
The Department provided $1.8 million to District Councils and local organisations to subsidise cleansing activities and campaigns organised to encourage community involvement in keeping Hong Kong clean.
Occupational Safety and Health
The Department is firmly committed to achieving a high standard of occupational safety and health (OSH) for all staff members at work, and has taken a number of OSH measures, including forming a Departmental Safety Management Committee and organising various promotional activities. In 2006, to further improve OSH standards, the Department undertook a number of initiatives, including:
- a high-level working group involving senior management held meetings regularly to monitor
injury-on-duty (IOD) situations and to discuss matters relating to OSH policy, improvement measures and, where necessary, individual IOD cases; - four consultancy service projects are being conducted namely, the development of Safety Management System in the Department; the development of OSH Improvement Measures for Hawker Control Teams; Workman II deployed in pest control, markets and cemeteries and crematoria services; and Foreman (Cleansing)/Senior Foreman (Cleansing) respectively; and also organisation of related training;
- tailor-made OSH training courses such as "Work Accident Prevention and Investigation" and "Certificate of Competence in Display Screen Equipment Assessment" have been organised;
- implementation of various measures, such as the provision of face shield and safety gloves, to enhance the OSH standard of refuse collection points;
- Personal Protective Equipment and Working Equipment Reference Materials have been drawn up for cleansing section and staff members concerned were provided with a copy of relevant information; and
- participation of the Departmental OSH Ambassador Team in 9 activities organised by the Occupational Safety and Health Council in 2006, including visits, seminars, and talks.





